
|
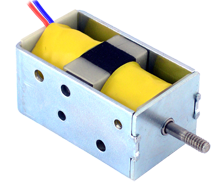
Magnetic Latching Solenoids
|
Latching solenoids are made with internal permanent magnets to hold the plunger in place once energized, so the solenoids can be left in the latched position indefinitely without consuming any power. The coil can be energized with a short pulse of voltage to move the plunger. No further power is needed when the plunger reaches the end of the stroke, as the attraction force of the permanent magnet will hold the plunger in place until it is released by another pulse of voltage. The bidirectional latching solenoids generally have two coils, one coil on each side with a common plunger. Applying a pulse to the left coil will cause the plunger to go to the left stop (pull) and latch in position. Applying a pulse to the right coil will cause the plunger to go to the right stop (push) and latch in position. The two coils can also be connected to each other in parallel (one pair of connection). Applying a pulse will cause the plunger to go to the left stop (pull) and latch in position. Reversing the polarity of the pulse will cause the plunger to go to the right stop (push) and latch in position. The unidirectional latching solenoids have one single coil. The plunger is pulled in with a pulse of voltage and held in the latched position with permanent magnets. The plunger can be released with a pulse with reverse polarity. |